Difference between revisions of "Using J-Link via WiFi"
(Created page with "This article explains different methods that can be used to connect to a J-Link and debug via WiFi. __TOC__ == J-Link WiFi == The J-Link WiFi comes with native WiFi support....") |
|||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== J-Link WiFi == |
== J-Link WiFi == |
||
| + | <br>[[File:J-Link-WiFi-Over-WiFi.png | thumb | right | 600px | Explanatory picture will follow shortly]] |
||
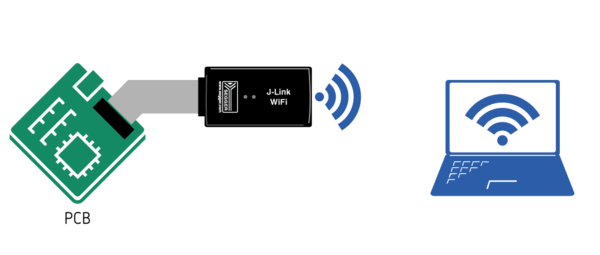
The J-Link WiFi comes with native WiFi support. |
The J-Link WiFi comes with native WiFi support. |
||
For detailed information on how to setup the J-Link WiFi, please refer to [[UM08001_J-Link_/_J-Trace_User_Guide#J-Link_WiFi_setup | this article]]. |
For detailed information on how to setup the J-Link WiFi, please refer to [[UM08001_J-Link_/_J-Trace_User_Guide#J-Link_WiFi_setup | this article]]. |
||
| + | <br clear=all> |
||
| + | == Via WiFi bridge == |
||
| − | == J-Link PRO and J-Trace PRO (Cortex-M) == |
||
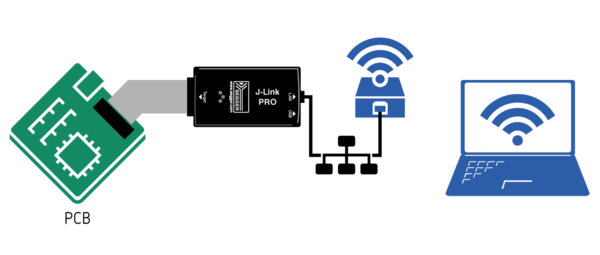
| + | [[File:J-Link-PRO-WiFi-Bridge.png | thumb | right | 600px | Schematic drawing showing how to connect to a J-Link PRO via WiFi]] |
||
| + | This way of WiFi-enable is supported by the following models: |
||
| + | * J-Link PRO |
||
| + | * J-Trace PRO |
||
The J-Link PRO and J-Trace PRO models have an Ethernet connector for wired Ethernet. |
The J-Link PRO and J-Trace PRO models have an Ethernet connector for wired Ethernet. |
||
| − | Therefore, making these models accessible via WiFi can be achieved |
+ | Therefore, making these models accessible via WiFi can be achieved by simply using a WiFi bridge. |
# Setup a WiFi bridge for the desired WiFi network. |
# Setup a WiFi bridge for the desired WiFi network. |
||
| − | # Power the J-Link PRO / J-Trace via a 5V USB power supply (e.g. |
+ | # Power the J-Link PRO / J-Trace via a 5V USB power supply (e.g. mobile powerbank). |
| − | # Connect the WiFi bridge to the Ethernet connector of the J-Link PRO |
+ | # Connect the WiFi bridge to the Ethernet connector of the J-Link PRO. |
| + | <br clear=all> |
||
| − | [[File:J-Link-PRO-WiFi-Bridge.png]] |
||
| − | == J-Link |
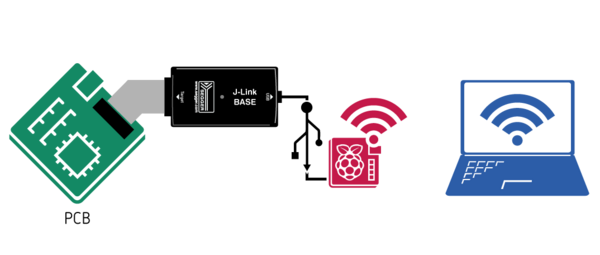
+ | == Via J-Link Remote Server == |
| + | [[File:J-Link-BASE-RasPi-Remoteserver.png | thumb | right | 600px | Explanatory picture will follow shortly]] |
||
| − | All other J-Link models do not come with native Ethernet support. |
||
| + | This way of WiFi-enable is supported by the following models: |
||
| − | However, it is still possible to make them accessible via WiFi. |
||
| + | * J-Link BASE |
||
| + | * J-Link PLUS |
||
| + | * J-Link ULTRA+ |
||
| + | * J-Link PRO |
||
| + | * J-Trace PRO |
||
The easiest and most commonly used method to do so is by using a Raspberry Pi (RasPi), running the [[J-Link Remote Server]]. |
The easiest and most commonly used method to do so is by using a Raspberry Pi (RasPi), running the [[J-Link Remote Server]]. |
||
| − | # Start the RasPi and connect it to the desired WiFi network |
+ | # Start the RasPi and connect it to the desired WiFi network. |
| − | # Install the [[J-Link Software Pack]] on the RasPi and the remote PC (available on the [https://www.segger.com/downloads/jlink#J-LinkSoftwareAndDocumentationPack|SEGGER homepage]) |
+ | # Install the [[J-Link Software Pack]] on the RasPi and the remote PC (available on the [https://www.segger.com/downloads/jlink#J-LinkSoftwareAndDocumentationPack|SEGGER homepage]). |
| − | # Connect the J-Link to the RasPi via USB |
+ | # Connect the J-Link to the RasPi via USB. |
| − | # Start the J-Link Remote Server on the RasPi and use it to connect to the J-Link |
+ | # Start the J-Link Remote Server on the RasPi and use it to connect to the J-Link. |
| + | # From the remote PC connect to the J-Link Remote Server on the RasPi as described in the [[J-Link_Remote_Server#Connecting_to_J-Link_using_J-Link_Remote_Server | J-Link Remote Server article]]. |
||
| − | # Install the J-Link Software Pack on the remote PC that is supposed to Control the J-Link |
||
| + | <br clear=all> |
||
| − | # From the remote PC connect to the J-Link Remote Server on the RasPi as described in the [[J-Link_Remote_Server#Connecting_to_J-Link_using_J-Link_Remote_Server | J-Link Remote Server article]] |
||
| − | {Note|This method works for all the latest J-Link models, and can also be used for J-Link PRO and J-Link WiFi} |
||
| − | [[File:J-Link-BASE-RasPi-Remoteserver.png]] |
||
Latest revision as of 15:57, 29 October 2021
This article explains different methods that can be used to connect to a J-Link and debug via WiFi.
J-Link WiFi
The J-Link WiFi comes with native WiFi support.
For detailed information on how to setup the J-Link WiFi, please refer to this article.
Via WiFi bridge
This way of WiFi-enable is supported by the following models:
- J-Link PRO
- J-Trace PRO
The J-Link PRO and J-Trace PRO models have an Ethernet connector for wired Ethernet. Therefore, making these models accessible via WiFi can be achieved by simply using a WiFi bridge.
- Setup a WiFi bridge for the desired WiFi network.
- Power the J-Link PRO / J-Trace via a 5V USB power supply (e.g. mobile powerbank).
- Connect the WiFi bridge to the Ethernet connector of the J-Link PRO.
Via J-Link Remote Server
This way of WiFi-enable is supported by the following models:
- J-Link BASE
- J-Link PLUS
- J-Link ULTRA+
- J-Link PRO
- J-Trace PRO
The easiest and most commonly used method to do so is by using a Raspberry Pi (RasPi), running the J-Link Remote Server.
- Start the RasPi and connect it to the desired WiFi network.
- Install the J-Link Software Pack on the RasPi and the remote PC (available on the homepage).
- Connect the J-Link to the RasPi via USB.
- Start the J-Link Remote Server on the RasPi and use it to connect to the J-Link.
- From the remote PC connect to the J-Link Remote Server on the RasPi as described in the J-Link Remote Server article.