Difference between revisions of "Arduino Due"
(→Example projects for SEGGER Embedded Studio) |
(→Debugging in SEGGER Embedded Studio) |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
[[File:Due_Connect.png|400px]] |
[[File:Due_Connect.png|400px]] |
||
| − | == Debugging |
+ | == Bare-metal Debugging == |
| − | === Example |
+ | === Example project for SEGGER Embedded Studio=== |
The following example project was created with the SEGGER Embedded Studio project wizard and runs out-of-the-box on the Arduino Due board. It is a simple Hello World sample and can be downloaded here: |
The following example project was created with the SEGGER Embedded Studio project wizard and runs out-of-the-box on the Arduino Due board. It is a simple Hello World sample and can be downloaded here: |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
If you want to revert the Arduino board to its original state you need to flash the Arduino bootloader of the corresponding board you are using. |
If you want to revert the Arduino board to its original state you need to flash the Arduino bootloader of the corresponding board you are using. |
||
For this the now established connection between your J-Link and the board can be used. |
For this the now established connection between your J-Link and the board can be used. |
||
| + | |||
| − | As a tool we recommend using J-Link Commander where you can use commands ''loadfile/loadbin'' to flash the bootloader file. If you are unsure where to get the bootloader from you can simply dump it into a binary file also using the J-Link Commander and the command ''savebin''. |
||
| + | Bootloader sources can be found here: |
||
| + | * https://github.com/arduino/ArduinoCore-samd/tree/master/bootloaders |
||
| + | * https://github.com/arduino/ArduinoCore-mbed/tree/master/bootloaders |
||
| + | |||
| + | As a tool we recommend using J-Link Commander where you can use commands ''loadfile/loadbin'' to flash the bootloader file. If the bootloader for your board should not be available you can simply dump it into a binary file also using the J-Link Commander and the command ''savebin''. |
||
For more information see our [https://wiki.segger.com/UM08001_J-Link_/_J-Trace_User_Guide J-Link user manual]. |
For more information see our [https://wiki.segger.com/UM08001_J-Link_/_J-Trace_User_Guide J-Link user manual]. |
||
Revision as of 09:31, 1 October 2020
This article describes how a J-Link probe can be used together with an Arduino Due board.
Contents
Minimum requirements
- Any J-Link
- J-Link software V6.86a or later
- Embedded Studio Version 5.10b or later
- A way to connect to the 10 pin debug connector of the Arduino Due board
Preparing for J-Link
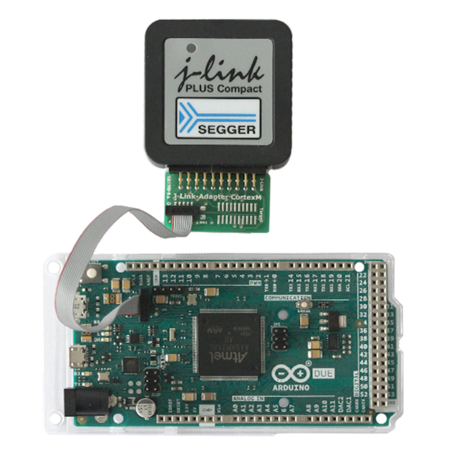
As the Arduino Due board comes with a presoldered 10-pin debug connector labeled JTAG all you need is a connector/adapter for that interface. If you are using the full size or compact models of J-Link the 9-Pin Cortex-M Adapter can be used. In this example we are using a J-Link Plus Compact. The resulting connection will then look like this:
- Power the board via one of the USB-Mini ports
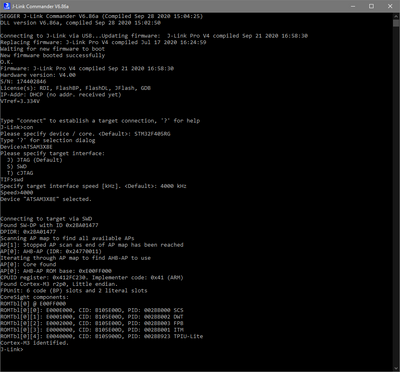
- Verify the Connection with e.g. J-Link Commander. The output should look as follows:
Bare-metal Debugging
Example project for SEGGER Embedded Studio
The following example project was created with the SEGGER Embedded Studio project wizard and runs out-of-the-box on the Arduino Due board. It is a simple Hello World sample and can be downloaded here:
Note: Using this example project will erase the Arduino bootloader and allow bare-metal debugging of the target device. If you want to revert the Arduino board to its original state you need to flash the Arduino bootloader of the corresponding board you are using. For this the now established connection between your J-Link and the board can be used.
Bootloader sources can be found here:
- https://github.com/arduino/ArduinoCore-samd/tree/master/bootloaders
- https://github.com/arduino/ArduinoCore-mbed/tree/master/bootloaders
As a tool we recommend using J-Link Commander where you can use commands loadfile/loadbin to flash the bootloader file. If the bootloader for your board should not be available you can simply dump it into a binary file also using the J-Link Commander and the command savebin. For more information see our J-Link user manual.