Difference between revisions of "RTT"
(→Stop mode) |
(→Stop mode) |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
[[File:Wiki-RTT_StopMode_JTAG_15MHz_256B.png|left|thumb|JTAG @ 15 MHz, reading 256 bytes, ~1.02ms halted time]] |
[[File:Wiki-RTT_StopMode_JTAG_15MHz_256B.png|left|thumb|JTAG @ 15 MHz, reading 256 bytes, ~1.02ms halted time]] |
||
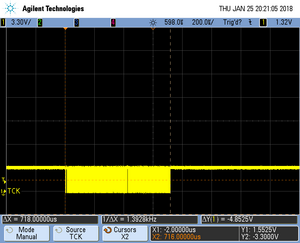
| − | [[File:Wiki-RTT_StopMode_JTAG_15MHz_1B.png| |
+ | [[File:Wiki-RTT_StopMode_JTAG_15MHz_1B.png|left|thumb|JTAG @ 15 MHz, reading 1 byte, ~718us halted time]] |
| + | <br> |
||
| − | |||
'''Cores with background mode support''' |
'''Cores with background mode support''' |
||
Revision as of 16:13, 25 January 2018
Contents
Modes
SEGGER RTT (SEGGER Real Time Transfer) can run in different modes where some modes are not available on all devices but other modes are which then have an impact on the real time behavior of the device.
Background mode
This is the mode which RTT was initially introduced with. In this mode, J-Link can access the memory of the target system while the MCU + application keeps running (background memory access), effectively not impacting the real time behavior of the application. In order to use this mode, the target MCU needs to support background memory accesses.
Cores with background mode support
- Cortex-M based devices (all cores from the series)
- Renesas RX based devices (all cores from the series)
Cores with optional background mode support
- Cortex-A based devices (all cores from the series)
- Cortex-R based devices (all cores from the series)
For Cortex-A/R it depends on the actual device if it supports background memory accesses because it is up to the device vendor if the necessary hardware unit is implemented or not. In addition to that, when using the background mode on Cortex-A/R based devices, some considerations need to be taken into account when it comes to caches etc. These are explained in AN08005
Stop mode
This mode has been introduced in J-Link software V6.30 in order to also allow using RTT on devices / CPU architectures that do not support background memory accesses. This mode affects the real time behavior of the application but can still be used for most applications.
In this mode, J-Link temporarily halts the CPU to access the memory and continues operation automatically after the memory access is done. The actual impact (halted time) on the real time behavior depends on the setup (target interface speed used, target interface used, length of JTAG chain, actual core that is used, ...).
Note: It is recommended to only use this mode with target interface speeds >= 12 MHz (J-Link PLUS, J-Link ULTRA+, J-Link PRO) to keep the effect on the real time behavior as small as possible. J-Link model overview
The following screenshots show typical halted times for an RTT stop mode access on a Cortex-A5 based device.
Cores with background mode support