Use SystemView without RTOS
SystemView works best when using it with one of our out-of-the-box supported RTOS' like embOS. However it is also possible to instrument a generic application without any RTOS present. That way SystemView can give deeper insight into any application type. The following article will explain how.
Contents
Prerequisites for the guide
- SystemView V2.52a or later
- Embedded Studio V3.40 or later
- Any J-Link/J-Trace debug probe
- Cortes-M Trace Reference Board or any other target hardware based on ST STM32F407
How to instrument a "NoOS" application with SystemView
The reference project which should be the result of this guide can be found here: Reference Project
The example description file for the example project can be found here: SYSVIEW_NoOS.txt
It is designed to be as generic as possible so any Cortex-M4 device can be used with that project. Just make sure that the target device name is changed accordingly.
GUIDE:
- Open Embedded Studio and create a new project for your device.
- Add SystemView Sources to your project. Specifically the folders /SEGGER, /Config and in this case the Sample/NoOS/Config/Cortex-M/SEGGER_SYSVIEW_Config_NoOS.c.
- Create a new file in the SystemView folder /Description called SYSVIEW_NoOS.txt, add all functions that shall be recorded with SystemView to that file with IDs starting at 33.
- Include SEGGER_SYSVIEW_Conf.h and SEGGER_SYSVIEW.h in your main.c.
- Edit SEGGER_SYSVIEW_ID_BASE to your actual RAM address on your device in SEGGER_SYSVIEW_Conf.h.
- In SEGGER_SYSVIEW_Config_NoOS.c. edit in function _cbSendSystemDesc(), SEGGER_SYSVIEW_SendSysDesc("N="SYSVIEW_APP_NAME",D="SYSVIEW_DEVICE_NAME); to SEGGER_SYSVIEW_SendSysDesc("N="SYSVIEW_APP_NAME",O=NoOS,D="SYSVIEW_DEVICE_NAME);
- In the same file edit SYSVIEW_RAM_BASE to the actual RAM Base address of your target device
- Call SEGGER_SYSVIEW_Conf(); and then SEGGER_SYSVIEW_Start(); in your main() function
- As this is a NoOS application the whole main() function will be treated as system idle, to enable this call SEGGER_SYSVIEW_OnIdle(); next.
- Optional: Initialize Systick in your main application. Use SEGGER_SYSVIEW_RecordEnterISR(); at the beginning of Systick_Handler and SEGGER_SYSVIEW_RecordExitISR(); at the end.
- Call the functions that shall be recorded in your application.
- In each function from the description list call SEGGER_SYSVIEW_RecordVoid(ID); first upon entry and SEGGER_SYSVIEW_RecordEndCall(ID); at the end of each function where ID is the ID number in your description file.
- Run your application and start a SystemView recoding.
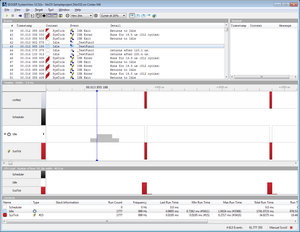
If everything was implemented as described your SystemView recording should look similar to the following picture:
Troubleshooting
I receive invalid packets. How can this happen?
- Invalid packets are mostly generated by the target system due to either one of two reasons:
- SystemView does not correctly lock when recording an event and is interrupted by another event. In this case make sure SEGGER_SYSVIEW_LOCK() and SEGGER_RTT_LOCK() are configured correctly for your device.
- The system goes into sleep or low-power mode and the J-Link cannot correctly access the RAM to read the SystemView buffer. It is recommended to not use WFI or any low-power mode while a debug probe is connected to the system.
I get overflow events when continuously recording. How can I prevent this?
- Overflow events occur when the SystemView RTT buffer is full. This can happen for following reasons:
- J-Link is kept busy by a debugger and cannot read the data fast enough.
- The target interface speed is too low to read the data fast enough.
- The application generates too many events to fit into the buffer.
- To prevent this:
- Minimize the interactions of the debugger with J-Link while the target is running. (i.e. disable live watches)
- Select a higher interface speed in all instances connected to J-Link. (i.e. The debugger and SystemView)
- Choose a larger buffer for SystemView. (1 - 4 kByte)
- Run SystemViewer stand-alone without a debugger.
My application crashes when I connect SystemView. What might be wrong?
- Make sure ~200 Bytes of stack are available for SystemView in every context (Task, Interrupt, Scheduler) which can create SystemView events.
I cannot start recording in SystemView. What might be wrong?
- Possible reasons are:
- J-Link or target is not connected: Make sure all connections are okay.
- The target is not running: Make sure the target is running, otherwise connection might fail or the RTT Control Block can not be found.
- The SystemView module is not configured: Make sure the SystemView module is included in your application and SEGGER_SYSVIEW_Conf() is called at the start of the application.
- The J-Link Software is out-of-date: Make sure you have the latest J-Link Software and Documentation Package installed.