Difference between revisions of "WSL"
(Added page regarding WSL) |
(Added screenshots) |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) is a part of Windows 10, that allows the user to run Linux applications on Windows. |
||
__TOC__ |
__TOC__ |
||
| − | Windows subsystem for Linux (WSL) is a part of Windows 10, that allows the user to run Linux applications on Windows. |
||
= J-Link specifics = |
= J-Link specifics = |
||
As of now WSL does not fully support USB devices. |
As of now WSL does not fully support USB devices. |
||
| − | In order to connect to a J-Link from WSL you either have to use the |
+ | In order to connect to a J-Link from WSL you either have to use the Ethernet / WiFi interface (if present, see [https://www.segger.com/products/debug-probes/j-link/models/model-overview/ Model overview]) |
or make use of the [[J-Link_Remote_Server | J-Link Remote Server ]] that runs on an another machine, capable of USB. |
or make use of the [[J-Link_Remote_Server | J-Link Remote Server ]] that runs on an another machine, capable of USB. |
||
| + | |||
| + | For more details please refer to the following article: |
||
| + | [[J-Link_Remote_Server#Connecting_to_J-Link_using_J-Link_Remote_Server | Connecting to J-Link using J-Link Remote Server]] |
||
== Example setup with USB == |
== Example setup with USB == |
||
| + | === J-Link Commander === |
||
| − | In this example we will connect to our J-Link (connected via USB) from WSL using the [[J-Link_Remote_Server | J-Link Remote Server ]] on the host side and the [[J-Link_Commander | J-Link Commander]] |
||
| + | In this example we will connect to our J-Link (connected via USB to the host) from WSL using the [[J-Link_Remote_Server | J-Link Remote Server ]] on the host side and the [[J-Link_Commander | J-Link Commander]] |
||
on the WSL side. |
on the WSL side. |
||
| − | === Requirements === |
+ | ==== Requirements ==== |
| + | * Windows 10 system which has the [[J-Link_Software_and_Documentation_Pack | J-Link Software and Documentation Pack]] installed |
||
| + | * WSL system which has the [[J-Link_Software_and_Documentation_Pack | J-Link Software and Documentation Pack]] installed |
||
* J-Link connected via USB to the host Windows 10 system |
* J-Link connected via USB to the host Windows 10 system |
||
| − | * WSL system that has the [[J-Link_Software_and_Documentation_Pack | J-Link Software and Documentation Pack]] installed |
||
| − | === Steps === |
+ | ==== Steps ==== |
| − | # Start the J-Link Remote Server in LAN mode on the Windows 10 host system. |
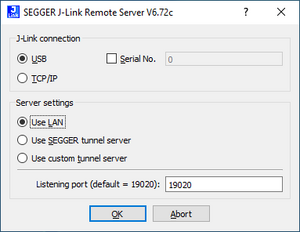
+ | # Start the J-Link Remote Server in LAN mode on the Windows 10 host system and select the correct J-Link if prompted.<br>[[File:JLinkRemoteServer_startup_screen.png|thumb|left| J-Link Remote Server: Startup screen]]<br clear=all> |
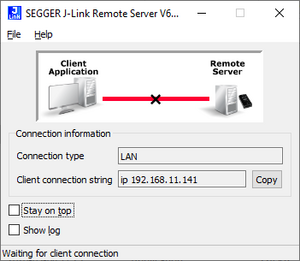
| + | # The J-Link Remote Server will now wait for incoming connections:<br>[[File:JLinkRemoteServer_lan_mode_waiting.png|thumb|left| J-Link Remote Server: Started and waiting for connections]]<br clear=all> |
||
| − | # Switch to the command-line prompt of your WSL Linux system |
||
| + | # Switch to the command-line prompt of your WSL Linux system. |
||
| − | # Insert your target device into the following command and execute it: |
||
| − | + | # Insert your target device and interface into the following command and execute it: '''JLinkExe -device <your-device> -ip localhost -if <target-interface> -speed 4000 -autoconnect 1''' |
|
| + | #* In this example we will connect to the NXP Kinetis K66 device on our [https://www.segger.com/evaluate-our-software/segger/empower/ emPower board], so the command would be as follows: '''JLinkExe -device MK66FN2M0XXX18 -ip localhost -if SWD -speed 4000 -autoconnect 1''' |
||
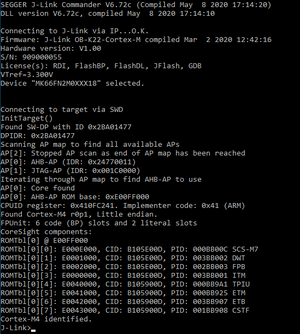
| + | # Now you should be able to make use of the [[J-Link_Commander#Commands | commands]] of the J-Link Commander.<br>[[File:JLinkCommander_MK66_connected.png|thumb|left| J-Link Commander: Connected to an NXP K66 MCU]] |
||
Latest revision as of 16:15, 14 May 2020
Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) is a part of Windows 10, that allows the user to run Linux applications on Windows.
Contents
J-Link specifics
As of now WSL does not fully support USB devices.
In order to connect to a J-Link from WSL you either have to use the Ethernet / WiFi interface (if present, see Model overview) or make use of the J-Link Remote Server that runs on an another machine, capable of USB.
For more details please refer to the following article: Connecting to J-Link using J-Link Remote Server
Example setup with USB
J-Link Commander
In this example we will connect to our J-Link (connected via USB to the host) from WSL using the J-Link Remote Server on the host side and the J-Link Commander on the WSL side.
Requirements
- Windows 10 system which has the J-Link Software and Documentation Pack installed
- WSL system which has the J-Link Software and Documentation Pack installed
- J-Link connected via USB to the host Windows 10 system
Steps
- Start the J-Link Remote Server in LAN mode on the Windows 10 host system and select the correct J-Link if prompted.
- The J-Link Remote Server will now wait for incoming connections:
- Switch to the command-line prompt of your WSL Linux system.
- Insert your target device and interface into the following command and execute it: JLinkExe -device <your-device> -ip localhost -if <target-interface> -speed 4000 -autoconnect 1
- In this example we will connect to the NXP Kinetis K66 device on our emPower board, so the command would be as follows: JLinkExe -device MK66FN2M0XXX18 -ip localhost -if SWD -speed 4000 -autoconnect 1
- Now you should be able to make use of the commands of the J-Link Commander.