Difference between revisions of "Arm trace technical specification"
(→Special case Cortex-M0+ trace) |
(→Minimum for pin tracing) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | When using the J-Trace PRO as a debugging tool it is crucial for a successful session that the trace data output by the microcontroller is meeting specific timing requirements. The trace clock speed (TRACECLK) is on most microcontrollers directly dependent on the CPU clock speed and is usually half of the CPU clock speed. |
+ | When using the J-Trace PRO as a debugging tool it is crucial for a successful session that the trace data output by the microcontroller is meeting specific timing requirements. The trace clock speed (TRACECLK) is on most microcontrollers directly dependent on the CPU clock speed and is usually half of the CPU clock speed. The following article will show the Arm trace timing requirements and which Arm Coresight components are required for which type of instruction tracing. |
__TOC__ |
__TOC__ |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
According to specification the maximum in spec trace clock is 100 MHz. But as there are some target devices that support even higher trace clock signals than that J-Trace Pro also supports higher trace clock speeds as explained in the note above. |
According to specification the maximum in spec trace clock is 100 MHz. But as there are some target devices that support even higher trace clock signals than that J-Trace Pro also supports higher trace clock speeds as explained in the note above. |
||
| + | |||
| + | {{Note|1=This trace specification assumes that all [[UM08001_J-Link_/_J-Trace_User_Guide#19-pin_JTAG.2FSWD_and_Trace_connector | 4 data pins]] are used in the trace interface. Only then an overflow free transmission can be guaranteed. Selecting 1 or 2 data pins to save pins can cause overflows depending on how much trace data the target application is creating. So it is recommended to use 4 data pins in your board design.}} |
||
== Solution for out of spec signals == |
== Solution for out of spec signals == |
||
| Line 43: | Line 45: | ||
=== Minimum for buffer trace === |
=== Minimum for buffer trace === |
||
| − | * [[ETM]] or PTM |
+ | * [[ETM]] or [[PTM]] |
* [[ETB]] or [[TMC | TMC/ETF]] |
* [[ETB]] or [[TMC | TMC/ETF]] |
||
=== Minimum for pin tracing === |
=== Minimum for pin tracing === |
||
| − | * Trace pins + [[ |
+ | * Trace pins + [[19-pin_JTAG/SWD_and_Trace_Connector | trace connector]] |
| − | * [[ETM]] or PTM |
+ | * [[ETM]] or [[PTM]] |
| − | * TPIU |
+ | * [[TPIU]] |
=== Optional for both setups === |
=== Optional for both setups === |
||
| − | * Trace funnel |
+ | * [[Trace funnel]] |
=== Special case Cortex-M0+ trace === |
=== Special case Cortex-M0+ trace === |
||
Latest revision as of 11:25, 3 April 2024
When using the J-Trace PRO as a debugging tool it is crucial for a successful session that the trace data output by the microcontroller is meeting specific timing requirements. The trace clock speed (TRACECLK) is on most microcontrollers directly dependent on the CPU clock speed and is usually half of the CPU clock speed. The following article will show the Arm trace timing requirements and which Arm Coresight components are required for which type of instruction tracing.
Contents
Arm trace timing requirements
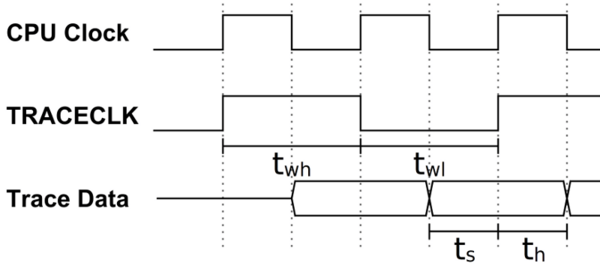
Arm defines the trace timing requirements as follows:
| Signal name | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| twl | TRACECLK LOW pulse width | Min. 2 ns |
| twh | TRACECLK HIGH pulse width | Min. 2 ns |
| tr/tf | Clock and data rise/fall time | Max. 3 ns |
| ts | Data setup time | Min. 3 ns |
| th | Data hold time | Min. 2 ns |
Note: J-Trace PRO has been designed to work with min. 1 ns ts and min. 1 ns th.
According to specification the maximum in spec trace clock is 100 MHz. But as there are some target devices that support even higher trace clock signals than that J-Trace Pro also supports higher trace clock speeds as explained in the note above.
This trace specification assumes that all 4 data pins are used in the trace interface. Only then an overflow free transmission can be guaranteed. Selecting 1 or 2 data pins to save pins can cause overflows depending on how much trace data the target application is creating. So it is recommended to use 4 data pins in your board design.
Solution for out of spec signals
In some rare cases devices supporting Embedded Trace Macrocell (ETM) trace are not outputting signals that fulfill the aforementioned timing requirements. To still make trace debugging available to the customer the J-Trace PRO has a so called Trace timing configuration feature which compensates wrongly output trace data signals.
Required trace components
Minimum for buffer trace
Minimum for pin tracing
- Trace pins + trace connector
- ETM or PTM
- TPIU